Ensuring proper drainage for retaining walls is essential for preserving their structural integrity and extending their lifespan. Incorporate a gravel layer, ideally 12 inches thick, composed of coarse, angular stones to facilitate water flow and prevent hydrostatic pressure buildup. Install perforated drainage pipes within this gravel layer to channel water away efficiently. Integrate geotextile fabric to separate soil and prevent clogging of drainage pathways. Employ weep holes as an additional measure to allow trapped water to escape. This careful integration of drainage materials and techniques can substantially enhance wall stability and mitigate the risks of erosion and saturation, fostering a robust and enduring structure.
Table of Contents
ToggleWalls Contractor Highlights
- Use gravel backfill to facilitate rapid water movement and reduce hydrostatic pressure behind the retaining wall.
- Integrate perforated drainage pipes to channel collected water away from the retaining structure.
- Install geotextiles to separate soil from drainage materials, preventing clogging and maintaining effective water flow.
- Ensure proper placement of weep holes to allow trapped water to escape, minimizing pressure build-up.
- Maintain a layer of angular stones to optimize compaction and interlocking for consistent drainage efficiency.
Defining Proper Wall Drainage
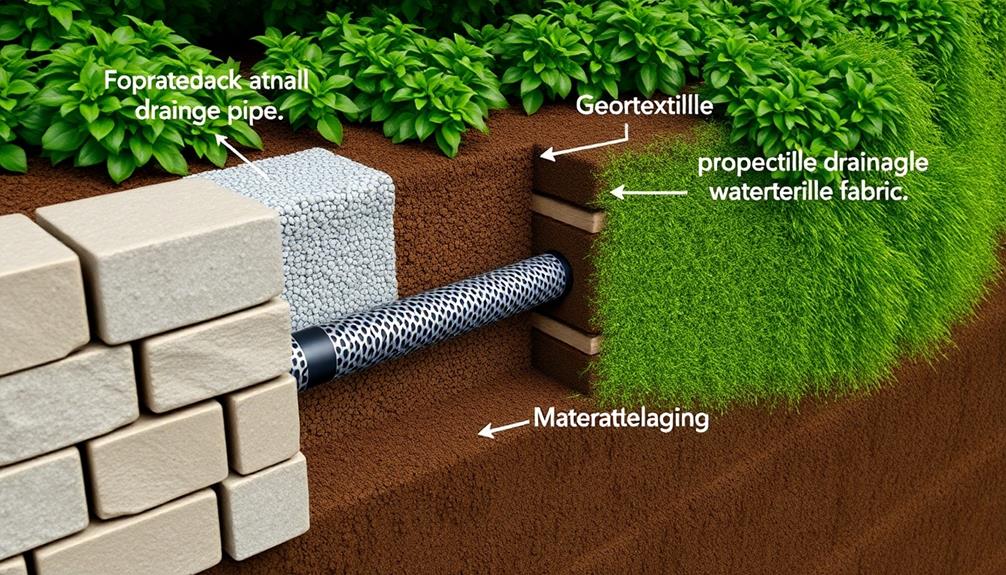
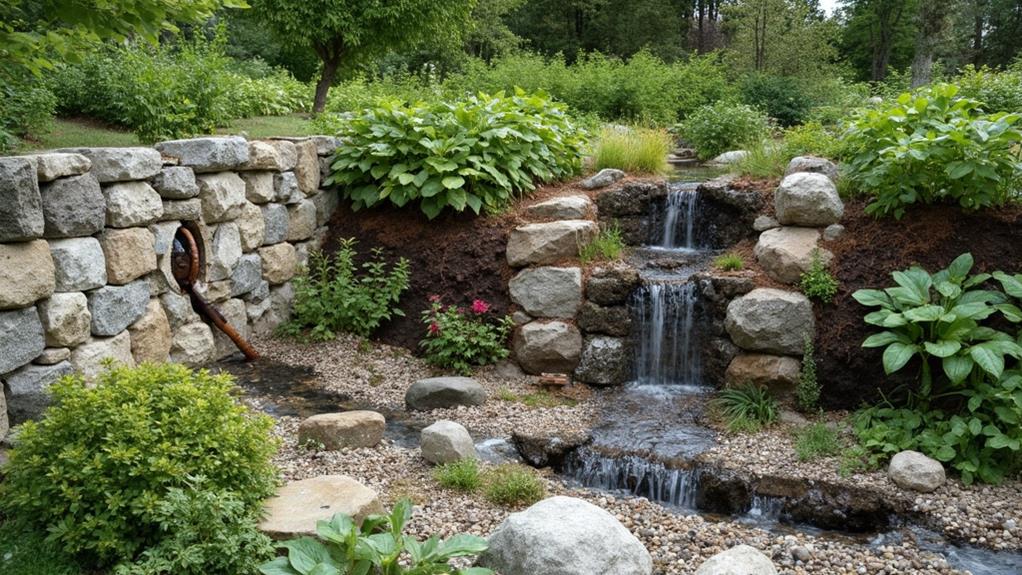
Proper wall drainage is a critical component in ensuring the longevity and stability of retaining structures, serving to mitigate the risks associated with water accumulation and hydrostatic pressure. By selecting the right drainage materials, such as gravel backfill, perforated drain pipes, and geotextile fabrics, one can prevent erosion on their property effectively.
Additionally, retaining walls, whether they are made from boulders, limestone, or fieldstone, require specialized installation expertise to incorporate drainage effectively and maintain structural integrity. Moreover, implementing effective drainage techniques, including the installation of weep holes and the incorporation of drainage systems at strategic intervals, contributes greatly to the prevention of erosion and soil saturation, thereby enhancing the durability of the retaining wall.
Importance of Wall Drainage
Effective drainage for retaining walls is essential to maintaining their structural integrity and longevity. Without adequate drainage, water accumulation behind these walls can lead to significant problems, compromising both their effectiveness and lifespan.
Water saturation in the soil exerting hydrostatic pressure is a key concern, ultimately causing undue stress on the wall structure. This pressure can lead to wall deformation, bulging, or even catastrophic failure, creating potential safety hazards and necessitating costly repairs.
Moreover, proper wall drainage safeguards against erosion, preventing the fine particles in the soil from being washed away. This erosion can undermine the base of the retaining wall, decreasing its stability and risking collapse. Soil integrity is hence preserved, providing a steadfast foundation vital for the wall's function and durability.
Additionally, ensuring effective drainage fosters a healthy landscape, as stagnant water can adversely affect plant life and create breeding grounds for pests, further deteriorating the surrounding environment. Retaining walls, as a result, act as guardians, maintaining not only the earth but the collective safety and aesthetic appeal of the shared spaces they protect. By emphasizing the significance of drainage, communities demonstrate their commitment to preserving both their environment and their infrastructural investments.
Essential Drainage Materials
To guarantee essential drainage for retaining walls, selecting the appropriate materials is indispensable for preventing water-related damages. The foundation of any effective drainage system lies in its choice of components, which collaboratively work to manage water flow and avert accumulation. Key materials such as gravel, geotextiles, and perforated drainage pipes play significant roles.
Gravel, due to its granular nature, facilitates rapid water movement, reducing hydrostatic pressure against the wall. When strategically placed behind the retaining structure, it forms a permeable barrier that guides water into designated channels.
Geotextiles, characterized by their fabric-like material, serve as an intermediary layer between soil and gravel. Their role extends to separating differing soil layers, thereby maintaining distinct drainage pathways. Additionally, employing a perforated drainage pipe at the base of the wall is indispensable; its designed openings allow collected water to be efficiently channeled away from the structure, ensuring stability and longevity.
Understanding and integrating these materials into the construction of retaining walls fosters a trusted community of homeowners and builders, united by a shared commitment to enduring craftsmanship and cohesive landscapes. Proper material choices not only guard against structural failures but also contribute to aesthetically pleasing environments.
Effective Drainage Techniques
Achieving optimal drainage for retaining walls frequently hinges on applying effective techniques tailored to site-specific conditions. The essence of proper drainage lies in managing both surface and subsurface water efficiently, preventing water accumulation and pressure that could compromise structural integrity.
Implementing successful drainage systems involves understanding the hydrological characteristics of the site and employing the right combination of tactics to assure ideal performance and longevity of the wall. To achieve this, the following techniques are commonly employed:
- Weep Holes: These openings are strategically placed within the retaining wall to allow trapped water to escape, reducing hydrostatic pressure behind the wall. They are essential in preventing water backflow which can weaken structures over time.
- Drainage Pipes: Laid behind the wall at its base, perforated drainage pipes collect and channel water away, thereby minimizing water buildup. This system is indispensable in maintaining soil stability and preventing erosion.
- Gravel Backfill: Utilizing gravel behind the wall improves drainage efficacy by promoting percolation, while reducing water retention and subsequent pressure on the structure.
- Filter Fabric: This barrier is used to separate soil from aggregate backfill, ensuring that sediment does not clog pipes or weep holes, thus preserving system effectiveness over time.
Employing these techniques ensures a welcoming environment for community spaces or private gardens, offering a sense of security and belonging through enduring structural performance.
Benefits

Proper drainage for retaining walls offers a multitude of benefits that contribute to the longevity and functionality of these structures. Effective drainage systems not only prevent water accumulation but also help alleviate erosion, which is indispensable for maintaining the integrity of the soil and the wall's foundation.
Prevents Water Accumulation
Effective drainage is essential in retaining walls as it plays a pivotal role in preventing water accumulation, which can have several benefits. When designing and maintaining retaining walls, attention to detail in drainage ensures the longevity and stability of these indispensable structures. By averting water buildup, wall integrity is preserved, and resources that might otherwise be spent on repairs or damage mitigation can be allocated elsewhere. Additionally, preventing water accumulation is a community-wide advantage, offering peace of mind to residents and businesses alike.
Consider the specific benefits of preventing water accumulation through effective drainage:
- Soil erosion prevention: Proper drainage channels water away from the wall foundation, keeping soil in place and minimizing erosion risks.
- Enhanced landscape health: By directing water flow appropriately, plant life near retaining walls receives ideal water supply without oversaturation.
- Longevity of wall materials: Drainage systems prevent moisture-related degradation, extending the life of wall components.
- Aesthetic maintenance: Reduced water pooling helps maintain the appearance of walls and surrounding areas, contributing positively to community beauty.
Through meticulous planning and attention to drainage in retaining wall construction, these benefits resonate with all stakeholders, fostering a sense of shared security and aesthetic pride.
Reduces Wall Pressure
Incorporating effective drainage systems in retaining walls greatly alleviates wall pressure, promoting structural stability. When water is not adequately diverted, hydrostatic pressure can build up behind the retaining structure. This pressure relentlessly exerts force against the wall, challenging its integrity and potentially leading to failure.
By integrating proficient drainage solutions, such as perforated pipes, gravel backfill, or filter fabrics, water is efficiently channeled away from the wall. This strategic redistribution lowers the pressure behind the wall, reducing the stress on the retaining structure and extending its lifespan.
The role of drainage in pressure reduction resonates deeply within communities aiming for durable and stable landscaping solutions. A sense of belonging emerges as individuals understand the mutual benefit of sound engineering practices that prioritize safety. These drainage solutions not only serve individual homeowners but enrich neighborhoods by maintaining smooth functionality and visual appeal of collective spaces.
Engaging with reliable engineering principles signifies an investment in both personal property and community welfare. Recognizing that proper drainage is essential in addressing unnecessary forces on retaining walls, stakeholders unite in the shared vision of resilience and dependability, fostering a supportive environment where structural harmony aligns with communal values.
Enhances Wall Stability
Reliability is a cornerstone of any well-constructed retaining wall, and amplified stability through effective drainage systems underscores this principle. By proficiently managing water flow, drainage systems prevent hydrostatic pressure build-up, a primary threat to the structural integrity of retaining walls. An expertly designed drainage solution fortifies the wall against natural elements, contributing to its longevity and robustness.
Trustworthy drainage systems promote stability in several ways:
- Optimal Load Distribution: Proper drainage guarantees uniform load distribution along the wall, mitigating differential settlement issues that can cause structural stress.
- Preventing Saturation: By diverting excess water away from the wall, effective drainage prevents soil saturation, which drastically reduces lateral pressure exerted by waterlogged soils.
- Preservation of Structural Material: Reducing moisture levels consequently curbs corrosion or decay of the wall materials, which bolsters the wall's physical integrity.
- Thermal Performance: Efficient drainage maintains a balanced moisture level, improving thermal performance and reducing freeze-thaw cycles that might compromise the wall's structural soundness.
For those immersed in the community of landscape construction professionals and homeowners alike, enhancing retaining wall stability through strategic drainage systems not only safeguards investments but also fosters a sense of shared stewardship over our built environments, guaranteeing they stand resilient against time and tide.
Minimizes Erosion Risk
While enhancing stability is a key advantage of proper drainage in retaining walls, another significant benefit lies in its ability to minimize erosion risk. Erosion, a natural process accelerated by inadequate drainage, can result in the gradual degradation of land and structures. When water accumulates behind retaining walls without a proper exit path, it exerts considerable pressure, which can weaken soil structure and exacerbate erosion. By implementing strategic drainage systems such as perforated pipes or gravel backfills, the accumulation of water is effectively redirected, mitigating the forces that lead to soil displacement.
Proper drainage creates a harmonious balance between human-imposed structures and natural elements. It guarantees that water, instead of becoming an adversarial agent of change, becomes a manageable component within the ecosystem. This seamless integration not only protects the integrity of retaining walls but also preserves the surrounding landscape, fostering a stable environment where communities can thrive. For those invested in long-term sustainability and the preservation of land value, embracing effective drainage solutions is more than a technical necessity; it is a commitment to safeguarding the environmental fabric that connects us to our surroundings, safeguarding the continued vitality of our collective spaces.
Include Drainage Gravel Layer
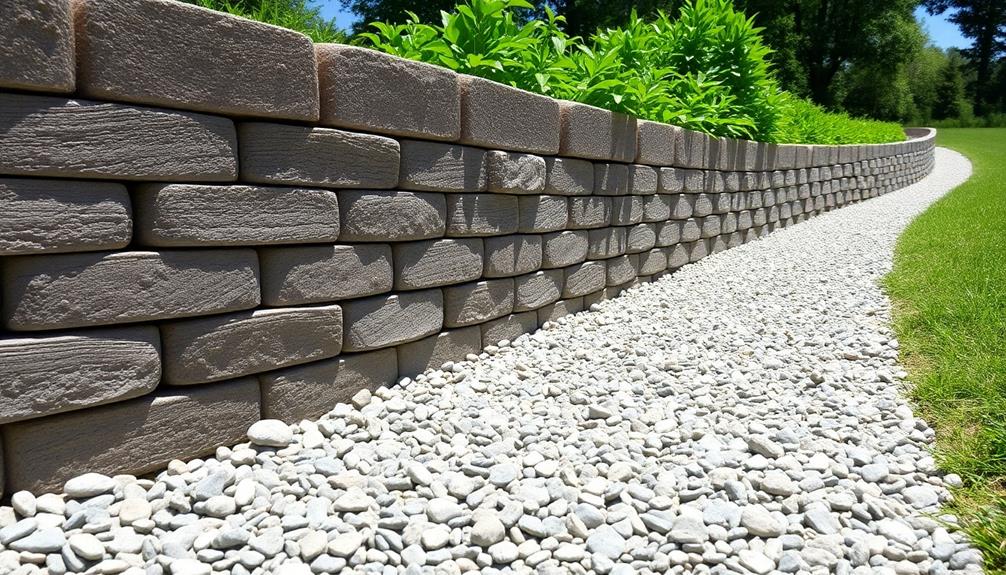

When constructing retaining walls, incorporating a drainage gravel layer is vital for maintaining structural integrity, as it not only facilitates effective water flow but also prevents hydrostatic pressure build-up. Choosing the right type of gravel and establishing the correct layer depth are essential factors that directly impact drainage efficiency. The following table summarizes the key considerations:
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Gravel Selection | Proper size and type for ideal drainage |
| Layer Depth | Adequate thickness to support water flow |
| Water Flow Channels | Designed to direct water away efficiently |
Importance of Gravel Selection
Selecting the appropriate gravel for drainage is crucial in guaranteeing the structural integrity and efficacy of retaining walls. An inadequate selection can lead to water accumulation, eventually compromising the wall's stability. To this end, the choice of gravel must prioritize characteristics conducive to optimal drainage.
The gravel's size is critical; typically, angular stones about 3/4 inch in diameter are preferred. This size facilitates ideal compaction and interlocking, promoting robust water flow.
Angular gravel, compared to rounded pebbles, provides better drainage due to the increased void space, allowing water to easily pass through and not get trapped.
Uniform distribution in gravel composition ensures consistent drainage. A mix of various sizes could prevent water from flowing freely, leading to pooling.
Granite, limestone, and crushed stone are commonly used for their resilience and permeability. These materials do not degrade easily and allow water to filter without obstruction.
Proper Gravel Layer Depth
Establishing the correct gravel layer depth is pivotal in guaranteeing the effective drainage and longevity of retaining walls. This foundational element not only supports the structural integrity but also facilitates optimal water movement, consequently preventing soil saturation and hydrostatic pressure, which can compromise the wall's stability.
Typically, a gravel layer depth of at least 12 to 24 inches is recommended behind the retaining wall. This measurement aims to provide an adequate buffer that allows water to percolate effectively, moving away from the wall structure. The drainage gravel layer should consist of angular, clean, and free-draining materials, with sizes ranging from ¾-inch to 1½-inch, guaranteeing gaps sufficient for water passage.
The gravel layer's primary function is to create a channel for water flow, diminishing the risks associated with soil erosion and displacement. This requires precise attention during installation to guarantee uniform depth across the entire length of the retaining wall. Additionally, incorporating a geotextile fabric between the soil and gravel layer can prevent soil particles from clogging the drainage system, maintaining its functionality over time.
Effective Water Flow Channels
Understanding the functionality of gravel layers inherently leads to the design of effective water flow channels, which are integral to proper retaining wall drainage. Gravel serves as both a filtration medium and a conduit for controlling water movement away from the retaining structure. These channels must be meticulously constructed to prevent hydrostatic pressure build-up that can compromise structural integrity. Employing a strategically placed gravel layer creates an avenue for water to be directed proficiently.
For ideal water flow management, consider the following steps:
- Select Quality Gravel: Utilize coarse, angular gravel, known for its superior void space, guaranteeing rapid water dispersal and minimizing blockages.
- Prepare Adequate Foundation: Before laying gravel, verify the foundation bed is properly graded to guide water in a specific direction, away from the retaining wall.
- Install Drainage Pipes: Perforate drainage pipes should be embedded within the gravel layer to direct water flow effectively, enhancing the gravel's filtering function.
- Implement Correct Thickness: Implement a gravel layer of at least 12 inches, to efficiently manage significant water volumes and prevent saturation near the retaining wall.
Walls Contractor FAQ
What Are Common Signs of Poor Drainage in Retaining Walls?
Common indicators of inadequate drainage in retaining walls include water pooling, efflorescence, wall tilting, and soil erosion. Addressing these signs promptly fosters safer environments, solidifying community ties through enhanced structural integrity and shared confidence in sustainable infrastructure solutions.
How Often Should French Drains in Retaining Walls Be Cleaned?
French drains behind retaining walls should ideally be inspected and cleaned every one to two years. Regular maintenance helps guarantee efficient water flow and mitigates potential damage, fostering structural integrity and longevity within your community's infrastructure.
Can Poor Drainage Affect the Lifespan of a Retaining Wall?
Yes, inadequate drainage can extensively compromise the lifespan of a retaining wall. Proper water management preserves structural integrity by preventing water accumulation and hydrostatic pressure, ensuring safety and longevity within communities that value secure and resilient infrastructure.
Are There Eco-Friendly Drainage Solutions for Retaining Walls?
Yes, eco-friendly drainage solutions like permeable backfill materials, geotextiles, and rain gardens can enhance sustainability. These methods offer effective water management, promoting community values and environmental stewardship while extending the lifespan of retaining walls.
What Role Does Landscaping Play in Retaining Wall Drainage?
Landscaping is vital in retaining wall drainage, as strategically placed vegetation can absorb excess water and reduce surface runoff. This approach fosters a sustainable community ethos, ensuring environmental harmony while maintaining structural integrity.







