In retaining wall construction, understanding soil composition and drainage is paramount to ensuring durability and stability. Soil texture, including sand, silt, and clay proportions, affects compaction and shear strength, influencing the wall's foundational support. Effective drainage is achieved through weep holes, drainage pipes, and layered gravel backfill, essential in preventing hydrostatic pressure and erosion. Integrating geotextiles aids in filtration and soil stabilization. Additionally, erosion control measures, such as geotextiles and vegetation, minimize soil loss and enhance structural integrity. These considerations not only protect the retaining wall's integrity but also enhance the managed landscape, inviting further exploration of these foundational elements.
Table of Contents
ToggleWalls Contractor Highlights
- Assess soil texture and composition to ensure proper drainage and stability for retaining wall construction.
- Implement drainage solutions like pipes and weep holes to manage water flow and prevent hydrostatic pressure on walls.
- Consider the use of geotextiles to enhance soil filtration and support drainage, prolonging the wall's lifespan.
- Evaluate soil's shear strength and cohesion to design a stable and supportive retaining wall system.
- Integrate gravel backfill layers to promote water percolation and prevent soil saturation behind retaining walls.
Considerations for Soil and Drainage
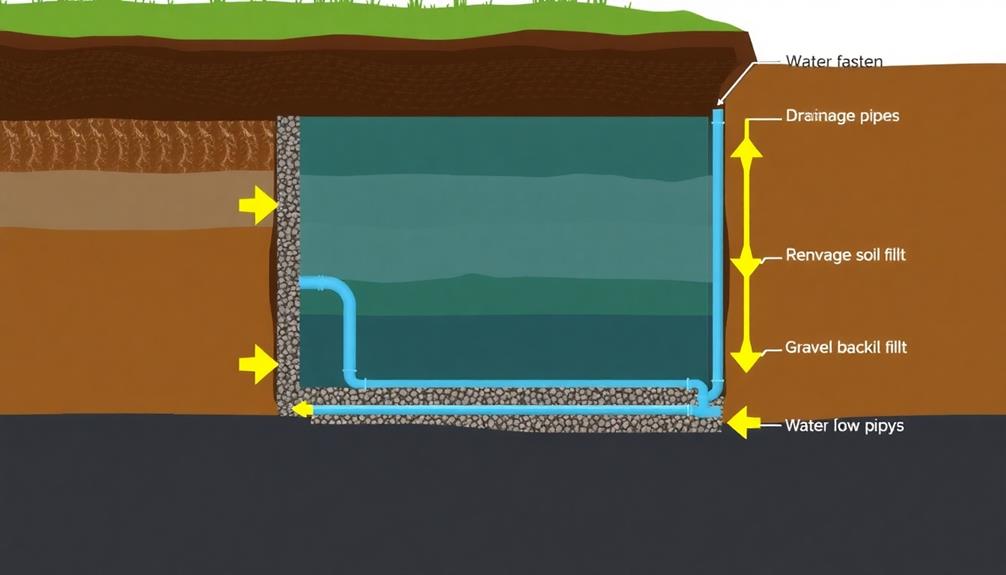
In considering the construction of a durable retaining wall, it is vital to first analyze the soil composition to ascertain load-bearing capability and stability. Depending on the type of retaining wall, such as boulder retaining walls, the specific soil type and reinforcement methods may vary to guarantee adequate support.
Adequate drainage solutions, such as incorporating gravel backfill and perforated pipe systems, mitigate hydrostatic pressure and prevent water accumulation, which can compromise wall integrity. Additionally, implementing effective erosion control techniques, such as geotextiles and vegetation, ensures long-term structural resilience and environmental compatibility.
Understanding the site's unique topography plays a key role in selecting the right materials and design for the wall's longevity.
Understanding Soil Composition
A fundamental understanding of soil composition is critical when designing an effective retaining wall, as the characteristics of the soil directly influence stability and drainage capabilities. Soil is a complex amalgamation of minerals, organic matter, water, and air, each component playing a crucial role in determining how the soil will interact with both natural and constructed systems. The proportions of sand, silt, and clay within the soil, termed its texture, greatly affect its drainage and compaction properties. Sandy soils, for instance, have large particles, allowing for excellent drainage but poor compaction; conversely, clay soils have tiny particles and exhibit poor drainage but high compaction capabilities.
The physical and chemical attributes of the soil must be meticulously assessed to guarantee the retaining wall is designed to withstand both soil pressures and environmental changes. Understanding such details fosters a sense of belonging within the design community, highlighting a commitment to resilience and sustainability. Importantly, the soil's shear strength and cohesion must be carefully evaluated, as they significantly impact the wall's ability to resist lateral pressures. Strategically considering factors such as the presence of organics or potential expansion behaviors will further validate that the wall remains durable and effective over time.
Effective Drainage Solutions
Properly implementing effective drainage solutions is paramount in guaranteeing the longevity and functionality of a retaining wall. Retaining walls are often tasked with holding back soil and managing water; without appropriate drainage, hydrostatic pressure can build up, leading to potential structural failures. The underlying principle of effective drainage is to alleviate this pressure by directing water away from the wall.
Incorporating weep holes, for instance, allows water to escape, reducing pressure buildup. In addition, the installation of a drainage pipe at the base further facilitates the movement of water away from the wall's foundation.
Strategically layered gravel backfill also plays a critical role in drainage. By promoting the percolation of water through its interstitial spaces, it prevents water from saturating the retained soil, minimizing pressure against the wall. Geotextiles, often used in conjunction with gravel, help to filter fine particles, maintaining the integrity and efficacy of the drainage system.
Understanding and effectively implementing these techniques fosters community among those involved in construction projects, as all stakeholders can appreciate the robust, cohesive functionality a well-designed retaining wall can provide. Such meticulous attention to detail guarantees that the retaining wall serves its purpose for decades.
Erosion Control Techniques
Although constructing an effective retaining wall safeguards against immediate soil displacement, erosion control techniques are indispensable in providing long-term stability. In the domain of soil preservation and drainage management, the integration of erosion control techniques enhances not only the integrity of the retaining structures but also fosters community resilience against environmental degradation.
Among the pantheon of strategies, geotextiles and erosion control blankets are prominent; these permeable fabrics serve multifaceted roles by filtering soil particles while allowing water to pass through, thereby mitigating erosion and ensuring structural soundness.
Furthermore, establishing vegetative covers presents an ecologically harmonious solution. The roots of well-chosen plants act as natural reinforcements, weaving through the soil to secure it in place, while the vegetative canopy shields the ground from direct precipitation impact, reducing surface runoff. Additionally, employing the terracing technique can effectively reduce slope angles, thereby decelerating the water flow and minimizing erosion risk.
Collectively, such techniques do more than fortify retaining walls; they contribute to a harmonious environment by promoting sustainability. When communities strategically implement these erosion control measures, they not only protect their immediate infrastructures but also foster a sense of stewardship over their shared natural resources.
Benefits

The construction of retaining walls presents numerous advantages, chief among them being the prevention of soil erosion, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of surrounding landscapes. Additionally, retaining walls aid in shoreline restoration by transforming and protecting waterfront areas from erosion and environmental factors.
These structures significantly enhance structural stability, providing essential support to vertical slopes and preventing potential land slippage, thereby ensuring safety and durability. Moreover, limestone walls can add an elegant and natural look to yards, contributing to improved landscape aesthetics.
Retaining walls can substantially increase property value, making them a wise investment for homeowners seeking both functional and visual enhancements to their outdoor spaces.
Prevents Soil Erosion
How do retaining walls effectively prevent soil erosion? Retaining walls serve as an invaluable tool in halting erosion, acting as a robust barricade between your landscape and the elements. By offering a reliable means to keep soil intact, they safeguard not only personal property but entire communities as well, creating a shared sense of security and unity. The role of these structures goes beyond mere functionality, enhancing both environmental sustainability and aesthetic harmony.
Protection of Community Spaces: Retaining walls maintain public parks and shared landscapes intact and accessible, fostering a sense of collective enjoyment.
Preservation of Ecosystems: They help maintain critical habitats by controlling sediment displacement, essential for preserving biodiversity.
Prevention of Property Damage: By mitigating soil movement, they avert issues such as land slippage, which can compromise buildings and infrastructure.
Stabilization of Landscapes: Retaining walls contribute considerably to maintaining the natural topography, preserving the unique character of areas we cherish.
The essence of belonging thrives when spaces we inhabit remain safe and unblemished. By investing in solutions that prevent soil erosion, we uphold the beauty and integrity of our shared environments, assuring they endure for generations.
Enhances Structural Stability
Retaining walls provide essential reinforcement to surrounding structures by enhancing their structural stability. Constructed with precision engineering, these walls resist lateral pressure from soil, water, and other earth materials. This solidifies the integrity of nearby infrastructures, such as buildings, roads, and essential landscaping elements.
In areas prone to soil movement or landslides, retaining walls safeguard that ground shifts do not compromise the foundational stability of valuable properties, fostering a sense of security for communities.
The construction process involves selecting materials that offer enduring strength, like concrete, stone, or steel, which are vital for withstanding immense pressure and environmental forces. Additionally, proper drainage systems are incorporated to prevent water accumulation and hydrostatic pressure, mitigating potential water damage. This approach not only guards against erosion but also maintains the wall's durability over time, providing long-term structural benefits.
Collaboration between engineers, architects, and construction teams is integral to designing walls that meet specific structural demands. By doing so, communities can confidently build and expand with the knowledge that their environment remains stable and resilient. Consequently, retaining walls not only provide physical strength but also nurture a collective reliance on sustainable and secure land development practices.
Improves Landscape Aesthetics
Design elements of retaining walls extend beyond their structural utility, enhancing the landscape aesthetics of surrounding areas. These structures provide opportunities for integrating natural beauty with functional design, creating harmony between human-made environments and the natural world. By carefully selecting materials and textures that complement existing elements, a retaining wall can transform an ordinary outdoor space into a visually mesmerizing area, fostering a sense of belonging among those who visit.
The aesthetic impact of retaining walls is significant, adding depth and interest to landscapes through varied heights and contours. This encourages exploration and interaction, inviting people to engage with their surroundings. The incorporation of thoughtful design elements can evoke emotional connections, enhancing the community experience.
- Natural stone finishes convey timeless charm, blending seamlessly into traditional landscapes.
- Contemporary geometric designs offer modern appeal, adding artistic flair to urban environments.
- Tiered levels create dynamic visual layers, perfect for showcasing diverse plantings.
- Integrated seating or planters foster community interaction, inviting neighbors to gather and connect.
Through such creative applications, retaining walls do more than merely manage soil and drainage; they enrich the landscape, resonating with those who seek environments that reflect both utility and artistry.
Increases Property Value
Enhancing the landscape with a well-designed retaining wall can lead to a considerable increase in property value. Beyond its visual appeal, a retaining wall fortifies the structural integrity of the property, mitigating risks such as erosion and flooding, which, if left unchecked, can depreciate property values. By incorporating these structures into your landscape, your property not only portrays an image of meticulous care but also reassures prospective buyers of its long-term stability and reduced maintenance concerns.
In today's real estate market, where first impressions are pivotal, properties adorned with aesthetically pleasing and functional features like retaining walls stand out dramatically. These walls can delineate garden beds, create tiered landscapes, and provide seating areas, transforming a mundane backyard into an inviting outdoor living space.
Such enhancements cater to a community-oriented audience that values shared experiences and leisure, potentially attracting buyers who appreciate the balance between functionality and beauty. Moreover, municipalities often value properties with effective land and water management solutions, acknowledging them as well-planned developments. This recognition can further impact property valuations, providing additional incentives for homeowners to invest in high-quality retaining wall construction, thereby nurturing a sense of belonging and achievement within their community.
Geotextile Fabric Application
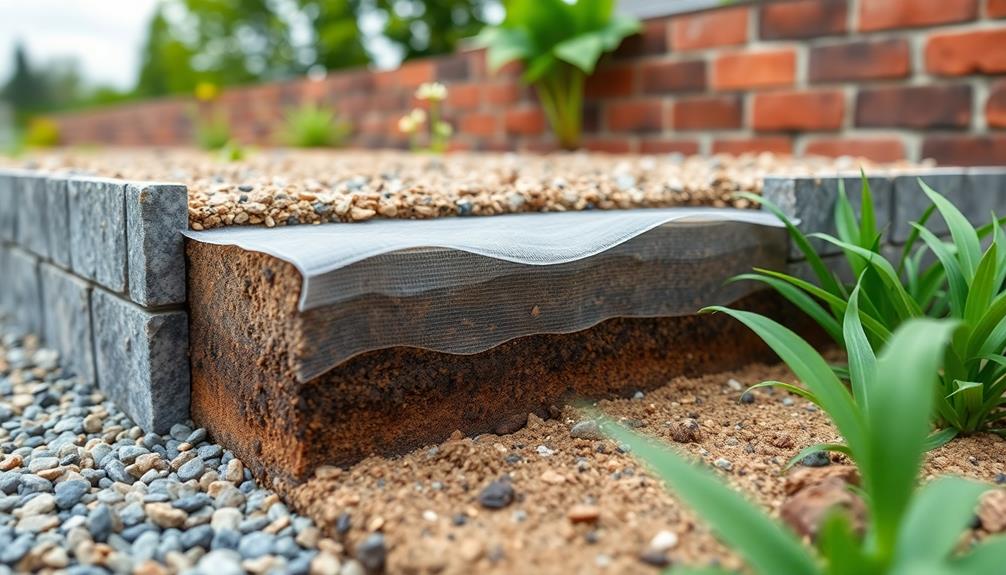

In the context of retaining wall construction, geotextile fabric plays a pivotal role by providing benefits such as erosion control and enhanced soil stabilization, which are essential for maintaining structural integrity. Understanding the various types of geotextile fabrics, from woven to non-woven options, can guide contractors in selecting the most suitable material for specific site conditions. Additionally, precise geotextile installation methods, tailored to factors like soil type and environmental conditions, help guarantee excellent performance and longevity of retaining walls.
| Benefits of Geotextile Fabric | Types of Geotextile Fabric | Geotextile Installation Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Erosion control | Woven | Consider soil type |
| Soil stabilization | Non-woven | Adjust for environmental factors |
| Extended longevity | Knitted | Ensure proper layering |
Benefits of Geotextile Fabric
While constructing retaining walls, the use of geotextile fabric offers significant advantages with respect to soil stability and water management. Serving as an integral component, geotextile fabric enhances the structural integrity of retaining walls by separating soil layers and promoting drainage, consequently preventing the buildup of hydrostatic pressure which can be detrimental to the wall's longevity. The multifunctionality of geotextile fabric truly underscores its importance in construction, offering comfort in its reliability and performance.
Enhanced Soil Stability: Geotextile fabric reinforces the soil, mitigating erosion and ensuring the soil remains compact and securely in place.
Effective Drainage: By facilitating water flow, geotextile fabric reduces water retention within the soil, which lowers the risk of seepage and structural failure.
Cost Efficiency: Implementing geotextile fabric can lead to significant savings over time due to reduced maintenance and extended lifespan of the wall.
Environmental Compatibility: Made from durable, permeable materials, geotextile fabric supports sustainable construction practices, which many communities cherish.
Types of Geotextile Fabric
Geotextile fabrics, vital in construction projects, vary in types that are suited to specific applications, ensuring ideal performance and endurance of retaining walls. Primarily, geotextiles are categorized into woven and non-woven fabrics, each serving a distinctive purpose.
Woven geotextiles, manufactured through the interlacing of fibers, are renowned for their high tensile strength. This quality makes them particularly advantageous in applications where soil stabilization is pivotal, effectively mitigating soil erosion and enhancing structural support. In contrast, non-woven geotextiles, produced through bonding fibers together using chemical or thermal means, emphasize filtration and drainage. Their permeability allows for efficient water flow, which is fundamental in preventing water buildup behind retaining walls.
The choice between woven and non-woven geotextiles relies on project-specific requirements. Factors such as soil type, anticipated loads, and environmental exposure should direct the selection process. For instance, in areas prone to heavy precipitation, non-woven geotextiles may offer superior water drainage capabilities, thereby maintaining the integrity of the retaining structure. Conversely, for terrains requiring heightened soil retention, woven fabrics are preferable. Understanding these distinctions fosters informed decision-making, promoting confidence in the geotechnical aspects of construction and ensuring the longevity and safety of retaining walls.
Geotextile Installation Tips
Successfully installing geotextile fabrics is essential for maximizing their functional benefits in retaining wall projects. These permeable textiles play a crucial role in providing separation, filtration, reinforcement, and protection, yet their correct application is indispensable to achieving these advantages. Precise installation practices can enhance the longevity and stability of retaining structures, providing added peace of mind and belonging to those involved in the project.
To guarantee successful geotextile application, consider the following tips:
- Surface Preparation: Prior to installation, confirm that the surface is smooth and free of sharp objects that could damage the fabric.
- Overlapping Layers: When using multiple sheets of geotextile fabric, overlap them by at least 300 mm (approx. 12 inches) to maintain continuity and strength.
- Anchoring: Secure the fabric in place with appropriate anchors or weights, particularly in areas susceptible to high winds or movement, preventing displacement.
- Tension and Alignment: Maintain consistent tension across the fabric, avoiding wrinkles to ensure even distribution of stress and effective filtration.
Walls Contractor FAQ
How Do Different Soil Types Affect Wall Longevity?
Soil types noticeably influence the durability of walls, with clay retaining moisture and exerting pressure, while sandy soils offer better drainage. Understanding soil characteristics fosters informed decisions, promoting structural integrity and community safety in wall construction projects.
Are There Specific Drainage Products Recommended for Retaining Walls?
Yes, specific drainage products, such as perforated pipes, geotextiles, and drainage mats, are recommended for retaining walls. These products help effectively manage water accumulation, preventing potential structural damage and enhancing the overall durability and performance of the retaining wall.
What Signs Indicate Poor Drainage in Retaining Walls?
Poor drainage in retaining walls can be identified by efflorescence, soil erosion, bulging, or cracking. Addressing these signs guarantees structural integrity, fostering community trust and inclusiveness in our shared commitment to safe, durable construction practices.
Can Plant Roots Damage the Retaining Wall Structure?
Plant roots can indeed compromise retaining wall structures. Roots exert pressure as they grow, causing displacement and potential cracking. Thoughtful landscaping choices and maintaining root barriers guarantee both structural integrity and aesthetic cohesion for sustainable community spaces.
Is Professional Consultation Necessary Before Starting Construction?
Engaging a professional consultant prior to commencing construction can provide invaluable insights, ensuring structural integrity, compliance with regulations, and ideal design. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of community among stakeholders, reducing risks and promoting project success.







