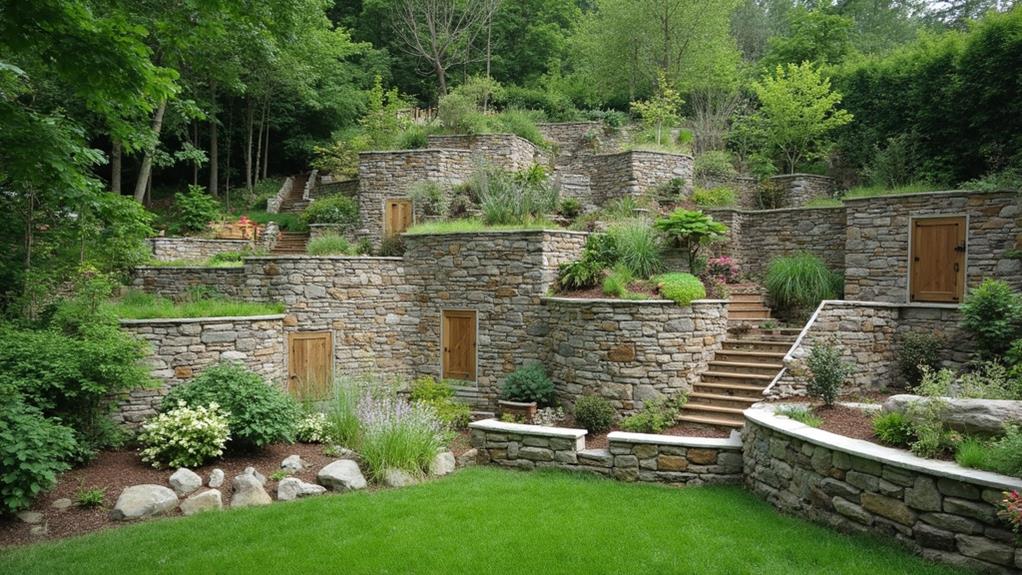
Common construction techniques for retaining walls focus on stability, load-bearing capacity, and aesthetic integration into the environment. Gravity walls utilize concrete, stone, or masonry, leveraging their weight to resist external forces, while reinforced soil systems combine soil with geosynthetics or metallic reinforcements, enhancing shear resistance and accommodating varying terrains. Anchored walls, incorporating minimal excavation, are particularly effective in urban and waterfront settings, enhancing stability and preventing landslides. These methods are dictated by soil characteristics, which influence structural choice and efficacy. Understanding these construction techniques is essential for achieving lasting structural integrity and harmony in landscaping projects.
Table of Contents
ToggleWalls Contractor Highlights
- Gravity walls use concrete, stone, or masonry, ideal for small to medium-sized projects with a simple design.
- Reinforced soil systems blend soil and reinforcing materials for increased stability on varied terrains.
- Anchored wall solutions need minimal excavation and offer enhanced stability for urban or waterfront sites.
- Construction technique choice for retaining walls depends on soil type, stability, and drainage needs.
- Effective retaining walls offer erosion control and structural stability, improving property value and aesthetics.
Most-Used Wall Construction Methods
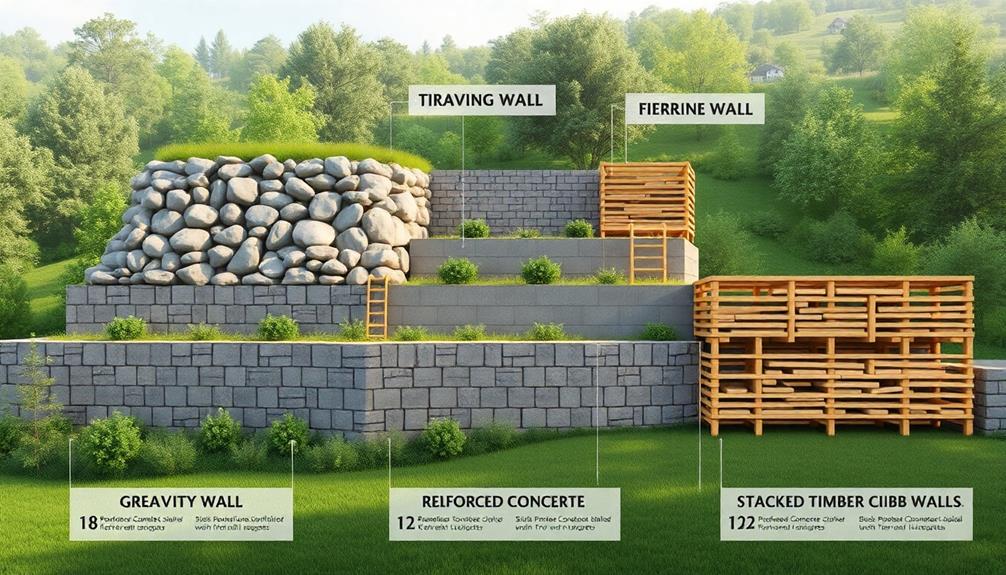
Retaining wall construction encompasses a variety of methods, each serving distinct structural and aesthetic purposes. For instance, boulder retaining walls make a powerful statement due to their size and natural appearance.
Gravity wall techniques leverage the weight and mass of the construction materials to resist lateral soil pressures, while reinforced soil systems integrate geosynthetics to enhance stability and improve bearing capacity. Additionally, anchored wall solutions employ cables or rods anchored into the soil or rock behind the face of the wall, providing additional support and increasing retaining capability in challenging terrain.
Gravity Wall Techniques
In the domain of construction, gravity wall techniques stand out as an essential method for building retaining walls, leveraging the wall's own weight to resist lateral earth pressure. These walls are typically crafted from concrete, stone, or masonry, providing a robust and durable solution. Their simplicity lies in the fact that they rely primarily on mass and weight, rather than intricate structural supports, making them particularly suitable for small to medium-sized retaining solutions. This inherent stability gives them an edge in situations where foundation conditions aren't ideal for deep anchoring.
Key features of gravity wall techniques include:
- Material Versatility: These walls can be constructed using a variety of materials, including natural stone, segmented concrete, and brick, offering aesthetic flexibility while ensuring strength.
- Ease of Construction: With straightforward design principles, they can often be assembled with minimal heavy machinery, reducing construction time and costs.
- Durability and Low Maintenance: Once established, gravity walls typically require little maintenance, standing resilient against natural elements.
- Environmental Integration: The use of natural materials allows these walls to blend seamlessly with existing landscapes, promoting an environmentally conscious construction approach.
This combination of functionality and form has made gravity walls a cornerstone in community-driven development projects, ensuring structural integrity while fostering a sense of belonging within the built environment.
Reinforced Soil Systems
Among the most prevalent methods for constructing retaining walls is the technique of reinforced soil systems. This method integrates the earth's natural stability with engineered reinforcement, creating a durable and robust structure.
The key to reinforced soil systems lies in the symbiotic relationship between soil and reinforcing materials, typically made of geosynthetics or metallic elements. These reinforcing elements are strategically embedded within the soil to augment its shear resistance and stability, enabling it to support greater loads and withstand environmental pressures.
These systems boast adaptability, as they can conform to various terrain and soil conditions, making them well-suited for diverse construction sites. Moreover, reinforced soil systems offer flexibility in design, allowing for the incorporation of various textures, colors, and vegetation, which helps blend the retaining wall into its natural surroundings.
This inclusive approach guarantees that the structure not only performs its functional role but also contributes to the aesthetic and environmental continuity of the area.
Anchored Wall Solutions
Building on the adaptability of reinforced soil systems, anchored wall solutions represent another frequently utilized technique in retaining wall construction. Characterized by their ability to provide exceptional stability to structures facing challenging environmental conditions, anchored walls employ anchors or tiebacks, which are embedded into the earth and tensioned for support. This approach is ideal when space constraints or existing structures necessitate minimal disturbance while maintaining wall integrity.
Anchored wall solutions exhibit several beneficial features:
- Minimal Excavation Requirements: Ideal for settings where deep excavation is impractical or restricted, preserving surrounding landscapes and pre-existing infrastructures.
- Enhanced Stability: The combination of wall friction and tensioned anchors mitigate slippage, ideal for areas prone to seismic activity or water pressure.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for diverse environments, including urban settings, roadside constructions, or waterfront developments, responding to varied architectural needs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Potentially reducing overall project costs by using existing materials on site and limiting fancy reinforcements, ensuring efficiency.
Ultimately, anchored wall solutions offer a strategic approach to retaining wall construction, aligning technical capabilities with the collective human aspiration for both progress and harmony within our built environment. Such methods not only safeguard structural interests but also weave our endeavors seamlessly within nature, fostering a balanced coexistence.
Benefits
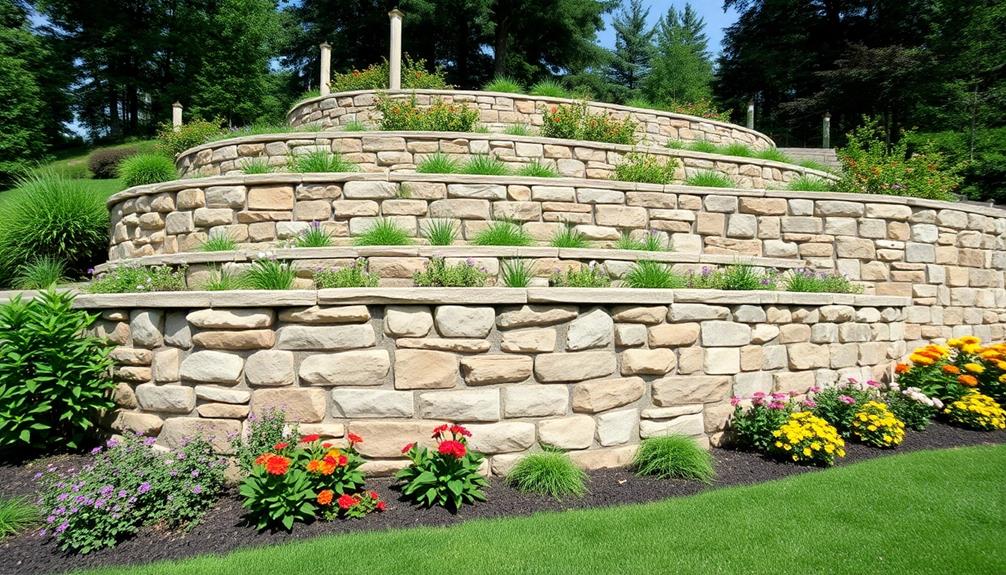

The construction of retaining walls presents significant benefits, foremost of which is their capacity to substantially improve structural stability by efficiently supporting soil laterally. Customizable dimensions of retaining walls allow for integration into various outdoor spaces, contributing to their versatility and appeal.
In addition to their practical purpose, these walls can be designed to enhance the aesthetic appeal of a property, thereby contributing to increased property value through thoughtful integration with the landscape. Additionally, the strategic implementation of retaining walls serves as an effective means of erosion control, preventing soil displacement and preserving the integrity of valuable land areas.
Improved Structural Stability
In the domain of construction, improved structural stability is a paramount consideration for retaining walls, offering substantial benefits. Retaining walls are tasked with holding back soil and preventing erosion, and consequently must be equipped to withstand the pressures exerted upon them over time. By focusing on structural stability, construction professionals can enhance the durability and longevity of these walls, ensuring they perform their intended function effectively.
Enhanced structural stability can lead to a multitude of advantages including:
- Increased Safety: Properly engineered retaining walls significantly reduce the risk of structural failure, thereby minimizing potential hazards to life and property.
- Longevity: Retaining walls constructed with stability in mind typically require fewer repairs and replacements over their lifespan, representing both cost-effectiveness and durability.
- Property Value: A structurally sound retaining wall contributes positively to property value by offering essential support and peace of mind to homeowners and builders alike.
- Environmental Protection: Stable retaining walls can effectively prevent soil erosion and landslides, safeguarding the surrounding landscape and ecosystems.
Enhanced Aesthetics Appeal
While often overlooked in functional design, incorporating aesthetic appeal into retaining walls can yield substantial benefits beyond their primary structural purposes. By carefully selecting materials, textures, and colors, retaining walls can be transformed into attractive landscape features that harmonize with their surroundings, fostering an environment that resonates with beauty and cohesion.
The design choices may include natural stone, decorative concrete, or wood, each offering unique visual and tactile experiences that enrich the garden or yard, providing a serene setting that encourages community interaction and personal reflection.
Engaging with professional designers and landscapers can offer tailored solutions, ensuring the retaining walls are not just functional but also aligned with the combined vision of homeowners and neighborhood aesthetics. This unity in design builds a collective identity, where communal spaces elicit a sense of belonging and pride among residents.
Additionally, the thoughtful integration of lighting or greenery around these structures can further enhance their visual impact. The result is a landscaped environment that not only serves practical purposes but also elevates the overall ambiance. Consequently, a well-designed retaining wall becomes more than a structural necessity; it transforms into an essential piece of living art within the landscape.
Increased Property Value
Beyond enhancing the visual appeal of a landscape, well-designed retaining walls can markedly contribute to boosting property value. A carefully crafted retaining wall not only serves as a functional element but also adds an element of sophistication and permanence to a property, ultimately enhancing its marketability. Prospective buyers often perceive retaining walls as a testament to the meticulous attention given to landscaping, a factor that profoundly improves the perceived value of the home.
Additionally, retaining walls can be an attractive selling point in regions where hilly or uneven terrain might pose challenges.
The benefits of retaining walls include:
- Increased Usable Space: Transforming sloped areas into flat, usable land can enhance outdoor living areas.
- Low Maintenance: Once constructed, retaining walls require minimal upkeep compared to other landscaping elements.
- Enhanced Curb Appeal: These structures lend an elegant, professionally landscaped appearance that attracts buyers.
- Durability and Longevity: Built to withstand environmental elements, retaining walls promise lasting value.
Effective Erosion Control
Retaining walls' strategic design plays a pivotal role in effective erosion control, offering both stability and protection against soil displacement. For communities facing the challenges of uneven terrain, retaining walls serve as essential structures that safeguard landscapes from the detrimental effects of erosion.
Beyond their structural integrity, these walls function as reliable guardians, preventing soil from washing away during rainfall or flooding events. The expert use of materials like concrete, timber, or stone not only guarantees durability but also provides a harmonious blend that complements the natural surroundings.
In regions with steep slopes, the implementation of retaining walls can vastly reduce the risk of land degradation. By hindering the movement of soil, these walls effectively preserve the integrity of the land, thereby fostering a sense of security and continuity for those residing in proximity.
Additionally, these structures help in managing water runoff, directing it appropriately and minimizing the impact on the surrounding environment. This element of control is paramount, as it supports plant growth on terraces that might otherwise succumb to erosion, enhancing both the aesthetic appeal and ecological stability of the area. Consequently, retaining walls are indispensable in cultivating environments that are both resilient and welcoming.
Soil Type Influences Technique
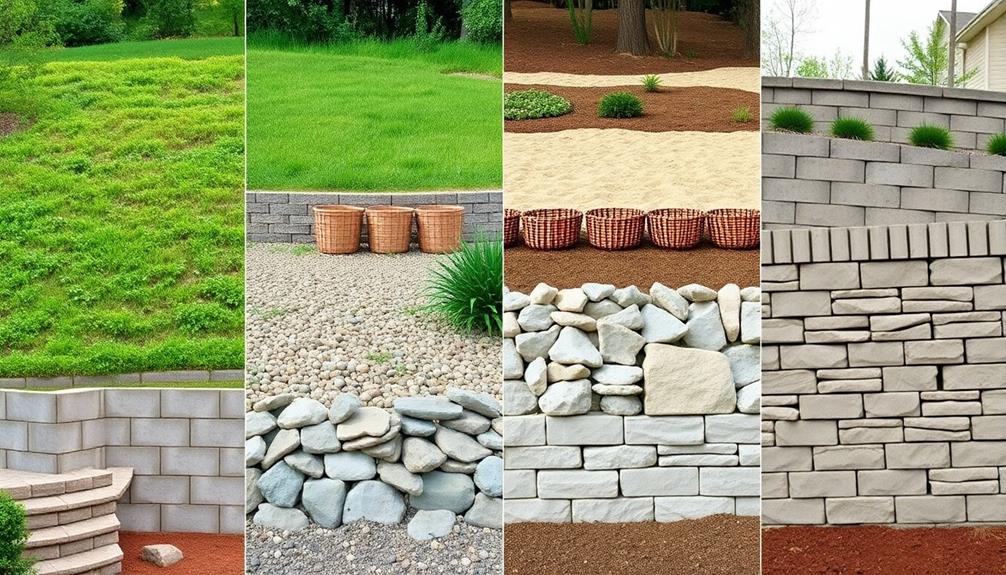

The choice of construction technique for retaining walls is heavily dictated by the type of soil present at the site, necessitating a rigorous assessment of soil stability, profound drainage considerations, and evaluation of load-bearing capacity to safeguard structural integrity. Understanding these factors is pivotal because variations in soil composition can dramatically affect the wall's performance, necessitating tailored approaches to design and implementation. The following table outlines key soil types and their corresponding considerations:
| Soil Type | Stability Assessment | Drainage Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Clay | Low to moderate stability | Poor natural drainage |
| Sandy | High stability | Excellent natural drainage |
| Silt | Low stability | Moderate natural drainage |
| Gravel | Very high stability | Good natural drainage |
Soil Stability Assessment
Evaluating soil stability is a fundamental step when determining the appropriate construction techniques for retaining walls, as the type of soil profoundly influences the choice of design and materials. Understanding the nuances of soil behavior ensures that the retaining wall will function effectively and safely over time. Engineers and architects must first assess the soil's mechanical properties to predict its stability under the weight of the wall.
When scrutinizing soil stability, several key factors come into play:
- Soil Composition: Identifying whether the soil is cohesive, such as clay, or granular, like sand, is indispensable, as each type behaves differently under stress.
- Load-Bearing Capacity: The soil's ability to support the weight of the retaining wall without significant displacement or failure is pivotal.
- Moisture Content: High moisture levels in soil can lead to increased weight and potential landslides, necessitating specific design adaptations.
- Slope Stability: The angle of the slope affects the lateral pressure exerted on the wall and must be carefully evaluated to avoid collapse.
These assessments enable the selection of tailored construction techniques, ensuring that the retaining wall integrates seamlessly into its environment. Through meticulous evaluation, the retaining structure can be a symbol of durability, thus instilling confidence and belonging within the community it serves.
Drainage Considerations
Effective drainage considerations are essential in retaining wall design, especially since different soil types demand tailored approaches. The significance of drainage cannot be overstated, as it directly influences the longevity and structural integrity of the retaining wall. Soil types, whether sandy, clayey, or silty, dictate how water permeates and accumulates behind the structure, necessitating careful selection of appropriate drainage solutions.
For instance, sandy soils, known for their excellent permeability, may require minimal drainage interventions, whereas clayey soils, notorious for poor drainage and high water retention, necessitate comprehensive drainage systems to mitigate hydrostatic pressure.
Integrating drainage components such as weep holes, perforated pipes, and drainage blankets enables the effective removal of excess water, preventing erosion and guaranteeing stability. Additionally, implementing geo-synthetics or filter fabrics can play a vital role in separating soil from drainage aggregates, thereby maintaining the system's functionality over time. Collective attention to these factors not only ensures that water is efficiently channeled away from the wall but also safeguards the wall from potential deformation or failure.
Load-Bearing Capacity
A retaining wall's success is deeply intertwined with understanding the load-bearing capacity of the soil it anchors into, as this dictates the appropriate construction technique. The soil's ability to support weight without excessive deformation is critical in preventing structural failure and ensuring long-term stability. Varying soil types, from cohesive clays to loose sands, greatly influence the design and construction approach, necessitating an assessment that informs material choice, structural design, and installation technique.
To appropriately address these considerations, several soil characteristics must be evaluated:
- Soil Composition: Determines cohesiveness and influences the wall's footing design.
- Moisture Content: Affects weight and stability; impacts drainage needs.
- Compaction: Influences bearing capacity and settling potential; affects wall stability.
- Slope Angles: Dictate earth pressure forces and can necessitate additional reinforcement.
Professionals are tasked with integrating their understanding of these elements into the wall's design process. By maximizing the soil's load-bearing capacity, they craft solutions that not only achieve structural integrity but also resonate with an aesthetic fitting for community environments. Through meticulous planning and implementation, retaining walls can serve as lasting emblems of strength and harmony within their surroundings.
Walls Contractor FAQ
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Retaining Wall Construction?
In retaining wall construction, commonly used materials include concrete blocks, poured concrete, timber, natural stone, and reinforced earth. These materials provide strength and durability, catering to a shared goal of building secure and lasting structures within communities.
How Does Weather Impact the Longevity of Retaining Walls?
Weather greatly impacts retaining wall longevity by influencing material durability. Freeze-thaw cycles, heavy rainfall, and erosion can weaken structures, while thermal expansion leads to cracks. Thoughtful design and regular maintenance are essential in fostering long-lasting, reliable retaining wall systems.
What Maintenance Is Required for Retaining Walls Over Time?
Regular maintenance of retaining walls includes inspecting for cracks, repairing structural damage, guaranteeing proper drainage systems function, and preventing erosion. By performing these tasks, the community secures durability, safety, and aesthetic appeal for the long-term stability of the structure.
Are There Specific Regulations for Building Retaining Walls in Urban Areas?
Urban areas often impose specific regulations for retaining wall construction, including considerations for height, materials, and drainage. Adherence to municipal codes guarantees safety and harmony within the community while fostering a sense of belonging through responsible development.
Can Retaining Walls Be Eco-Friendly and if So, How?
Retaining walls can indeed be eco-friendly by utilizing sustainable materials like recycled concrete, incorporating native vegetation for stabilization, and employing permeable designs that promote water infiltration, fostering a sense of community commitment toward environmental stewardship and harmony.







