Retaining wall construction is governed by a thorough set of regulations to guarantee structural integrity, public safety, and environmental protection. These regulations typically encompass soil stabilization techniques, reinforcement materials, and drainage system design. Local building codes mandate specific requirements for wall height, setbacks, and soil stability assessments. Contractors must obtain necessary permits, submit engineered designs for approval, and undergo periodic inspections throughout the construction process. Adherence to these regulations is paramount for maximizing the benefits of retaining walls, including erosion control, space optimization, and aesthetic enhancement. Understanding the full scope of these regulations can greatly impact project success and long-term stability.
Table of Contents
ToggleWalls Contractor Highlights
- Local building codes dictate design specifications, materials, and construction methods for retaining walls.
- Permits are typically required for walls exceeding a certain height, often 3-4 feet, depending on jurisdiction.
- Soil stability assessments and engineered plans are mandatory for larger retaining wall projects.
- Drainage systems must comply with local regulations to prevent erosion and ensure wall stability.
- Regular inspections during construction are required to verify compliance with approved plans and safety standards.
Structural Support for Slopes

When constructing retaining walls to provide structural support for slopes, engineers must consider a range of essential factors to guarantee stability and longevity. These considerations include implementing appropriate soil stabilization techniques, selecting suitable reinforcement materials, and designing effective drainage systems to manage water flow and pressure.
Boulder retaining walls offer a durable and long-lasting solution for supporting slopes, making a powerful statement with their size and natural appearance. By carefully addressing these critical elements, construction professionals can create robust retaining walls that effectively support slopes while minimizing the risk of failure and maximizing the structure's lifespan.
Soil Stabilization Techniques
Three primary soil stabilization techniques provide structural support for slopes in retaining wall construction: mechanical stabilization, chemical stabilization, and biological stabilization. Mechanical stabilization involves the use of geosynthetic materials, such as geogrids or geotextiles, to reinforce soil layers and increase their load-bearing capacity. This method is particularly effective in areas with poor soil conditions or steep slopes.
Chemical stabilization utilizes various additives, including lime, cement, or fly ash, to alter the physical and chemical properties of the soil, enhancing its strength and reducing its susceptibility to erosion. This technique is often employed in clay-rich soils or when rapid stabilization is required. Biological stabilization harnesses the power of vegetation to reinforce soil structure through root systems and reduce surface erosion. This eco-friendly approach is ideal for projects prioritizing natural aesthetics and long-term environmental sustainability.
Engineers must carefully assess site-specific factors, such as soil composition, moisture content, and anticipated loads, to determine the most appropriate stabilization technique or combination of methods for each retaining wall project. By implementing these soil stabilization techniques, construction professionals can guarantee the longevity and structural integrity of retaining walls while optimizing slope stability and overall project performance.
Reinforcement Materials
Building upon the foundation of soil stabilization techniques, reinforcement materials play a pivotal role in providing structural support for slopes in retaining wall construction. These materials enhance the structural integrity of retaining walls, allowing them to withstand significant lateral earth pressures and maintain long-term stability. Various reinforcement options are available, each with specific advantages and applications depending on the project requirements and site conditions.
Common reinforcement materials utilized in retaining wall construction include:
- Geosynthetics (e.g., geogrids, geotextiles)
- Steel reinforcement bars and mesh
- Soil nails and ground anchors
- Mechanically stabilized earth (MSE) systems
- Fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs)
The selection of appropriate reinforcement materials is essential to ensuring the retaining wall's performance and longevity. Factors such as soil type, wall height, surcharge loads, and environmental conditions must be carefully considered during the design process. Engineers and contractors must adhere to local building codes and industry standards when specifying and installing reinforcement materials.
Proper installation techniques, including correct spacing, embedment depth, and connection to the wall face, are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of these structural support elements.
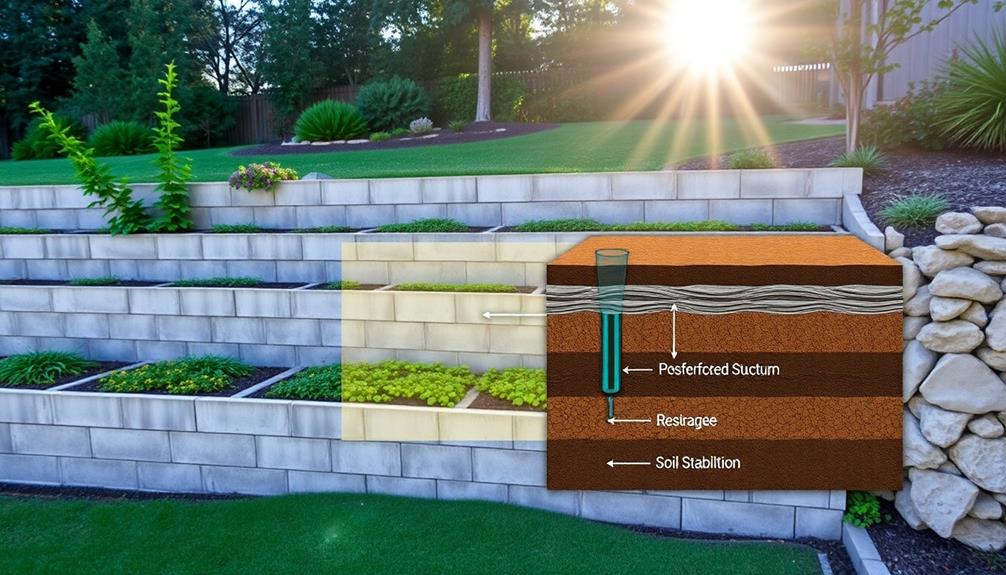
Drainage System Design
A well-designed drainage system is crucial for guaranteeing the long-term stability and performance of retaining walls. Proper drainage management mitigates hydrostatic pressure buildup behind the wall, which can lead to structural failure if left unchecked. Regulatory bodies typically mandate specific drainage requirements, including the installation of weep holes, geotextile filters, and drainage pipes.
When designing a retaining wall's drainage system, engineers must consider factors such as soil composition, anticipated water flow, and climatic conditions. A thorough approach involves incorporating both surface and subsurface drainage components. Surface drainage systems, such as swales and berms, divert water away from the wall's vicinity, while subsurface systems, including perforated pipes and granular backfill, facilitate water removal from behind the structure.
Regulatory standards often dictate minimum pipe diameters, spacing of weep holes, and specifications for filter fabrics to prevent soil erosion. Additionally, many jurisdictions require the implementation of erosion control measures during construction to protect neighboring properties and waterways. By adhering to these regulatory guidelines and employing best practices in drainage system design, contractors can guarantee the longevity and stability of retaining walls, safeguarding both property and public safety.
Benefits
Retaining walls offer numerous benefits that extend beyond their primary function of structural support. These structures can markedly improve property value by creating visually appealing landscaping features while simultaneously providing essential erosion control for sloped areas.
Boulder walls, in particular, offer a sustainable and eco-friendly solution for landscaping and erosion control, requiring minimal maintenance compared to other options. Additionally, retaining walls maximize usable space on properties with challenging topography, allowing homeowners to transform previously unusable terrain into functional outdoor living areas with aesthetic appeal.
Improved Property Value
Well-constructed retaining walls can substantially enhance a property's value by improving both its functionality and aesthetic appeal. These structures not only prevent soil erosion and create usable space on sloped terrain but also contribute to the overall landscaping design.
Homeowners and property investors alike recognize the long-term benefits of properly installed retaining walls, which can dramatically increase a property's market value.
The value-adding potential of retaining walls stems from several factors:
- Increased usable land area
- Enhanced landscape design and curb appeal
- Improved drainage and erosion control
- Creation of outdoor living spaces or gardens
- Structural support for buildings on sloped sites
When constructed in compliance with local regulations and engineering standards, retaining walls become valuable assets to a property. They transform challenging terrains into functional spaces, allowing for expanded outdoor living areas, tiered gardens, or additional parking.
In addition, the visual impact of well-designed retaining walls can profoundly improve a property's overall appearance, making it more attractive to potential buyers or renters. This combination of practical utility and aesthetic enhancement contributes to a higher property valuation, making retaining walls a wise investment for those looking to maximize their real estate assets.
Erosion Control
One of the primary benefits of retaining walls is their significant role in erosion control. These structures effectively combat soil displacement caused by natural elements such as wind, water, and gravity. By stabilizing slopes and containing soil, retaining walls prevent the gradual loss of land that can occur over time, especially in areas with steep inclines or frequent precipitation.
Retaining walls serve as a pivotal line of defense against erosion by redirecting water flow and reducing its velocity. This process minimizes soil saturation and subsequent runoff, which are major contributors to erosion. In addition, these walls provide an opportunity for strategic landscaping, allowing property owners to integrate plants and drainage systems that further enhance erosion control measures.
For communities and individual property owners alike, implementing retaining walls as part of an extensive erosion control strategy can yield long-term benefits. These include preserving valuable topsoil, maintaining landscape integrity, and protecting structures from potential damage caused by shifting ground. By investing in well-designed retaining walls, individuals and communities demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship and sustainable land management practices, ensuring the longevity and stability of their properties for years to come.
Enhanced Usable Space
Beyond their structural and erosion control functions, retaining walls offer a significant advantage in maximizing usable space on properties with challenging topography. By strategically implementing these structures, property owners can transform steep slopes or uneven terrain into functional areas, effectively expanding their usable land. This enhancement of space can be particularly beneficial in urban or suburban environments where land is at a premium.
Retaining walls can create:
- Level areas for gardens or outdoor living spaces
- Terraced landscapes for aesthetically pleasing designs
- Additional parking or driveway space
- Expanded building footprints for home additions or outbuildings
- Raised planting beds for improved landscaping options
The creation of these newly functional areas not only increases property value but also enhances the overall quality of life for residents. By carefully considering local zoning regulations and obtaining necessary permits, property owners can leverage retaining walls to optimize their land use. This approach allows for the development of previously underutilized portions of a property, providing opportunities for outdoor entertainment, gardening, or simply expanding living space. As land becomes increasingly scarce in many areas, the ability to maximize usable space through retaining wall construction becomes an invaluable asset for property owners and developers alike.
Aesthetic Appeal
While retaining walls serve practical purposes in maximizing usable space, they also offer significant aesthetic benefits to property owners. These structures can be designed to complement and enhance the overall landscape, creating visually appealing outdoor environments that seamlessly blend form and function. By incorporating various materials, textures, and colors, retaining walls can become striking focal points or subtle accents within a property's design scheme.
Skilled landscapers and architects often utilize retaining walls to create multi-level gardens, terraced patios, or elevated seating areas that add depth and interest to otherwise flat terrain. The strategic placement of these walls can frame picturesque views, define outdoor living spaces, and establish a sense of privacy and enclosure.
In addition, retaining walls can be adorned with cascading plants, integrated lighting fixtures, or decorative elements such as built-in planters or water features, further elevating their aesthetic value. When properly designed and constructed, these structures not only prevent soil erosion and manage drainage but also contribute to the overall curb appeal and market value of a property, making them a worthwhile investment for homeowners seeking to create cohesive and visually striking outdoor spaces.
Permitting and Zoning Requirements
When constructing a retaining wall, adhering to local permitting and zoning requirements is imperative for legal compliance and structural integrity. These regulations typically encompass local code compliance, height and setback rules, and mandatory soil stability assessments. Understanding and following these requirements not only guarantees the safety of the structure but also prevents potential legal issues and costly modifications down the line.
| Requirement | Description | Typical Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| Local Code Compliance | Adherence to specific building codes | Detailed construction plans |
| Height and Setback Rules | Restrictions on wall dimensions and placement | Site surveys and architectural drawings |
| Soil Stability Assessments | Evaluation of ground conditions | Geotechnical reports and soil tests |
Local Code Compliance
Local code compliance is a critical aspect of retaining wall construction that builders must address before breaking ground. Municipalities often have specific regulations governing the design, materials, and construction methods for retaining walls. These codes are typically based on factors such as soil conditions, wall height, and proximity to property lines or structures.
To guarantee compliance, builders should:
- Obtain and review the latest version of local building codes
- Consult with a licensed engineer for complex projects
- Submit detailed plans and calculations for review
- Schedule required inspections throughout the construction process
- Maintain accurate documentation of all approvals and inspections
Adhering to local codes not only guarantees the safety and longevity of the retaining wall but also protects builders from potential legal and financial liabilities. It is paramount to recognize that code requirements may vary significantly between jurisdictions, even within the same region. Builders must familiarize themselves with the specific regulations in each area where they work. This attention to detail demonstrates a commitment to quality and professionalism, fostering trust with clients and regulatory authorities alike.
Height and Setback Rules
Most municipalities impose strict height and setback regulations for retaining wall construction, which are fundamental aspects of permitting and zoning requirements. These regulations are designed to guarantee structural integrity, safety, and aesthetic cohesion within communities.
Typically, retaining walls exceeding four feet in height require engineered plans and specific permits, while those under this threshold may have more lenient requirements. However, it's important to consult local ordinances, as some jurisdictions may have lower height limits or additional stipulations.
Setback rules dictate the minimum distance a retaining wall must be positioned from property lines, streets, and other structures. These requirements vary widely depending on the wall's height, location, and surrounding land use. For instance, walls adjacent to public rights-of-way often have more stringent setback requirements than those on private property.
Additionally, many localities mandate increased setbacks for taller walls or those built on sloped terrain. Compliance with these regulations is necessary not only for legal construction but also for maintaining harmonious relationships with neighbors and preserving community standards. Homeowners and contractors must thoroughly research and adhere to these height and setback rules to avoid costly penalties or mandatory alterations.
Soil Stability Assessments
Soil stability assessments play an essential role in the permitting and zoning requirements for retaining wall construction. These evaluations are pivotal for ensuring the safety and longevity of the structure, as well as compliance with local regulations. Geotechnical engineers conduct comprehensive analyses of the soil conditions to determine the wall's design parameters and potential risks.
The assessment typically includes:
- Soil classification and stratification
- Bearing capacity evaluation
- Slope stability analysis
- Groundwater assessment
- Seismic hazard analysis
Results from these assessments inform imperative design decisions, such as foundation depth, drainage systems, and reinforcement requirements. Local authorities often mandate specific soil stability criteria that must be met before issuing construction permits. These requirements may vary based on factors like wall height, proximity to property lines, and local geological conditions.
For property owners and contractors, understanding and adhering to these soil stability regulations is paramount. Failure to comply can result in project delays, increased costs, or even legal consequences. By prioritizing thorough soil stability assessments, we collectively contribute to safer, more resilient communities and protect our investments in infrastructure.
Walls Contractor FAQ
What Materials Are Best for Retaining Walls in Coastal Areas?
For retaining walls in coastal areas, we recommend marine-grade materials that resist corrosion and salt damage. Concrete blocks, treated timber, and natural stone are excellent choices. Additionally, consider using geotextile fabrics for improved drainage and structural integrity.
How Often Should Retaining Walls Be Inspected for Safety?
Regular inspection of retaining walls is vital for our community's safety. Experts recommend annual checks, with more frequent inspections after severe weather events. Together, we can guarantee the longevity and stability of these important structures in our neighborhoods.
Can Retaining Walls Be Used to Create Raised Garden Beds?
Many gardening enthusiasts use retaining walls to create beautiful raised garden beds. These structures not only add visual interest to your outdoor space but also provide excellent drainage and soil depth for your plants to thrive.
Are There Eco-Friendly Alternatives to Traditional Retaining Wall Materials?
Eco-friendly alternatives for retaining walls include recycled plastic lumber, gabion walls filled with local stones, reclaimed wood, and living walls with plants. These options not only support sustainability but also create a unique, natural aesthetic for your landscaping project.
How Do Freeze-Thaw Cycles Affect Retaining Wall Longevity and Maintenance?
Freeze-thaw cycles vitally impact retaining wall durability. As members of our community, we should be aware that these cycles can cause cracking, shifting, and deterioration. Regular inspections and proper drainage are indispensable for maintaining our walls' integrity and longevity.







